
SQL Queries
2022, Apr 04
Sql Language Theory
SQL Notes.
- Origins IBM’s research labs.
- Early 1970’s.
- SQL (Structure Query Language).
Database (DB)
- Database.- A collection of integrated records (any collection of related information).
- Record.- A representation of a conceptual object.
- Database consists of data and metadata.
- DB’s can be stored in different ways.
Database Management Systems (DBMS)
- SQL is just a language, and there for special software needs to be used in order to perform queries.
- A query is a question you ask the database.
- DBMS.- Is a special software or program that helps users create and maintain a database.
- It makes it easy to manage large amounts of information.
- Handles security, backups, import/export of data.
DBMS Diagram
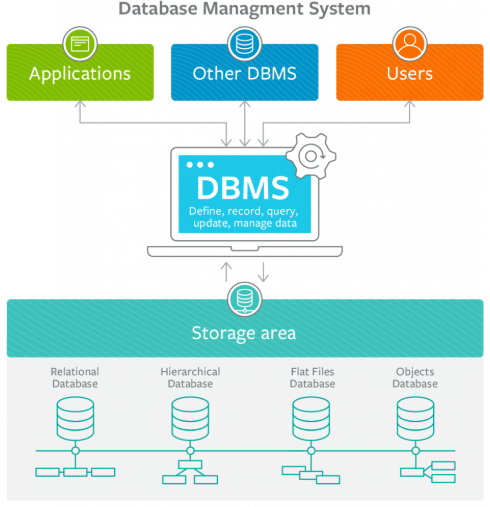
Reference for the image. 1
Types of Databases
- Relational Databases (SQL) - Organize data intone or more tables. - Each table has columns and rows. - A unique key identifies each row.
- Non-Relational Databases (No SQL, not just SQL) -Organize data is anything but traditional table. - key: value stores. - Documents (JSON, XML, BLOB, etc.) - Flexible tables. - graphs, key-value hash, keys mapped into values.
Software
Relational Databases Management Systems (RDMMS)
- Helps users create and maintain a relational database.
- MySQL, Oracle, Postgre SQL, Maria DB, etc.
- Uses the structured query language.
- Used to perform CRUD (create, read, update, delete).
- Used to define tables and structures.
- SQL code is not always portable between applications without modification.
Non-Relational Databases Management Systems (NRDMMS)
- Helps users create and maintain a non-relational database.
- MongoDB, DynamoDB, apache Cassandra, firebase, etc.
- Implementation is specific.
- Any non-relational database falls under this category, so there is no set standard language.
- Most NRDMMS will implement their own language in order to perform CRUD, on the database.
Database Queries
- Queries are requests made to the database management system for specific information.
- As the database’s structure becomes more and more complex, it becomes more difficult to retrieve specific pieces of information.
- Queries are instructions given to the RDBMS in SQL.
Keys
- Relational databases always have a primary key, which can be the column id. Other keys are surrogate, natural, and foreign keys.
- Natural keys are used with the same purpose like in the real world.
- Foreign keys are links to other databases or tables and mark a relationship between databases and tables.
SQL
- SQL is a language used for interacting with relational databases management systems.
- You can use SQL to get the RDBMS to do things fir you. Like CRUD.
- Create, manage, design, administrate tasks, implements. etc.
- SQL implementations vary between systems.
- Concepts are the same, but implementation may vary.
SQL Types
- SQL can be referred as a hybrid language with 4 basic types of language
- Data Query Language (DQL) used to query the database for data.
- Data Definition Language (DDL) used for defining database schemas.
- Data Control Language (DCL) used for controlling access to the data in the database.
- Data Manipulation Language (DML) used for inserting, updating, and deleting data from the database.
SQL data types
- Int integer number.
- Decimal (M,N) float point number.
- Varchar string.
- BLOB binary language object.
- Date yyyy-mm-day
- Timestamp yyyy-mm-day and h
 sec
sec
Table creation
/*table creation, data types int(integer),
varchar (string with 20 chars)
*/
CREATE TABLE student (
student_id INT,
name VARCHAR(20),
major VARCHAR(20),
primary key(student_id) /*primary key; can also go in the student_id int*/
);Insert data into database by inserting the values in order of appeareance. You can not insert duplicate keys, beacuse a record all rady exists.
INSERT INTO student VALUES(1,'Jack','Biology');
INSERT INTO student VALUES(2,'Kate','Sociology');We can specify the picies of information eg. only student_id & name.
INSERT INTO student(student_id,name) VALUES(3,'Claire');Now we drop the table.
DROP TABLE student;The full code is:
/*table creation, data types int(integer),
varchar (string with 20 chars)
*/
create table student (
student_id int,
name varchar(20),
major varchar(20),
primary key(student_id) /*primary key; can also go in the student_id int*/
);
--Insert data into database by inserting the values in order of appeareance.
--You can not insert duplicate keys, beacuse a record all rady exists.
INSERT into student values(1,'Jack','Biology');
INSERT into student values(2,'Kate','Sociology');
/*We can specify the picies of information eg. only student_id & name*/
INSERT into student(student_id,name) values(3,'Claire');
/* adding more*/
INSERT into student values(4,'Jack','Biology');
INSERT into student values(5,'Mike','Copmuter Science');
select * from student;--selection of all elements from student table
-- now we drop the table.
drop table student;
--adding a not null and unique instruction in the table.
--unique is if a repeated name is used it will not be allowed
create table student (
student_id int,
name varchar(20) not null,
major varchar(20) unique,
primary key(student_id) /*primary key; can also go in the student_id int*/
);
select * from student;
--adding
INSERT into student values(1,'Jack','Biology');
INSERT into student values(2,'Kate','Sociology');
--cannot insert a null value because it is specified in the table
INSERT into student values(3,null,'Chemistry');
--cannot add a double entry because unique is instructed. hence the error.
INSERT into student values(4,'Jack','Biology');
--not null and unique are refered as constrains.
drop table student;
--another constrain is the defualt value, which is used when no value is entered.
create table student (
student_id int,
name varchar(20),
major varchar(20) default 'undicided',
primary key(student_id) /*primary key; can also go in the student_id int*/
);
--not adding a value will be replaced with the default value.
insert into student(student_id,name) values(1,'Jack');
--seing the table.
select * from student;
--drop the table.
drop table student;
--another is the auto increment for the student id, like i++.
create table student (
student_id int auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
major varchar(20) default 'undicided',
primary key(student_id) /*primary key; can also go in the student_id int*/
);
--adding only the name and major.
insert into student(name,major) values('Jack','Biology');
insert into student(name,major) values('Kate','Sociology');
--seeing the table, with theincremented id´s.
select * from student;-
Reference: https://www.bmc.com/blogs/dbms-database-management-systems/ ↩